The swift transition from the Information Age to the Intelligence Age is drastically altering the way organizations handle talent acquisition and development. Today, Chief Human Resources Officers (CHROs) are confronted with the pressing task of integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into their strategies to stay competitive.
Notably, generative AI holds the promise of transforming cognitive skills, akin to the steam engine’s impact on mechanical abilities. This transition necessitates a thorough overhaul of workforce strategies to fully harness AI’s potential. It involves not just incorporating AI tools but also fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptability among employees.
By doing so, organizations can ensure they are well-equipped to thrive in this new era of AI-driven innovation. Adapting to these changes is paramount for organizations aiming to maintain a competitive edge and sustain growth in the Intelligence Age. This comprehensive approach is essential for organizations to harness AI’s capabilities and ensure enduring success.
As leaders of workforce strategy, CHROs play a pivotal role in guiding their organizations’ adaptation to an AI-powered future. Their leadership is vital in promoting AI adoption while managing change sensitively across all levels of the organization.
Specifically, CHROs must focus on four key areas:
By championing AI’s immense potential as a catalyst for innovation and positive transformation, CHROs can elevate HR to the forefront of value creation within their organizations.
Talent acquisition lies at the core of organizational success. As competitive pressures intensify globally, the need for efficient, unbiased hiring practices has become more critical than ever. AI introduces transformative potential to identify and attract top talent quickly.
Specifically, AI-based recruitment tools can: 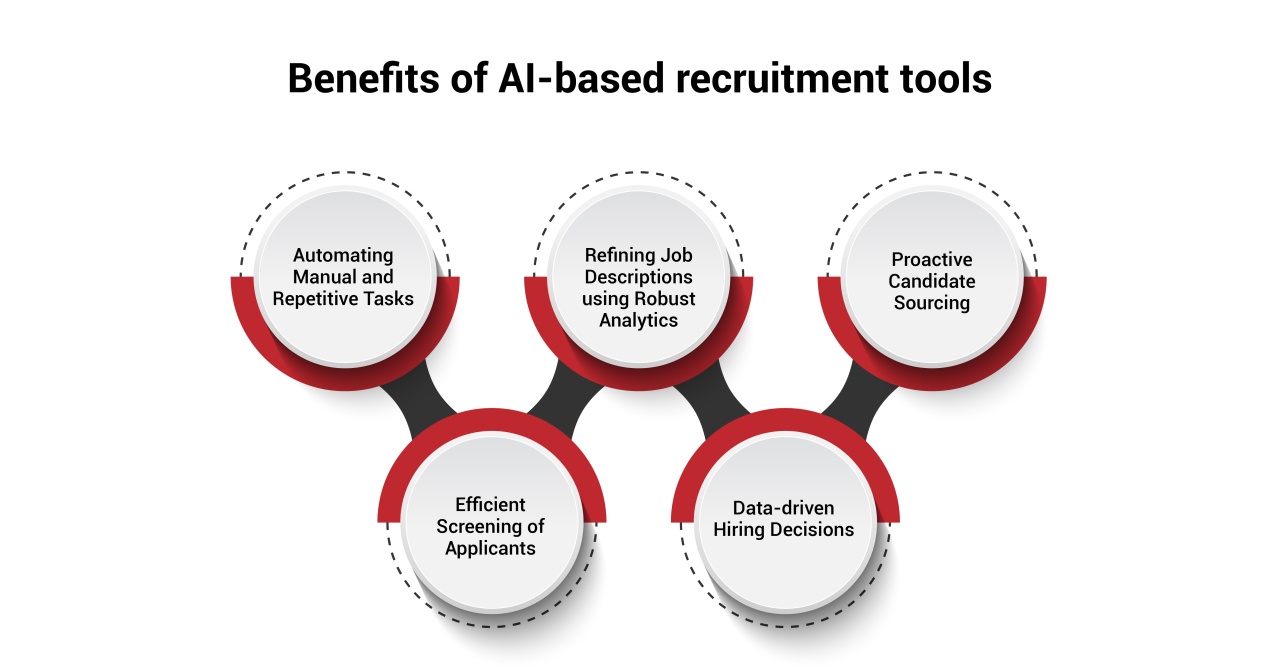
A significant proportion of recruiters' time is spent on repetitive administrative tasks such as scheduling interviews, sending rejection emails, and consolidating applicant information from various sources. By automating these mundane activities, AI frees up recruiters' bandwidth to focus on more strategic hiring decisions.
AI-based scheduling tools like X.ai and Clara can autonomously coordinate interviews and meetings between hiring managers and candidates. These tools can track real-time availability across stakeholders' calendars and propose optimal time slots after consulting with all parties via email.
Additionally, chatbots and email bots can handle the task of sending routine communications to candidates, providing updates on applications or conveying rejection decisions through personalized templates. For instance, the Ideal chatbot allows recruiters to automate their entire communication workflows, saving hours of manual efforts.
On the coordination aspect, AI-based applicant tracking systems like Greenhouse provide centralized dashboards to manage candidates' progress. Built-in analytics consolidate essential data such as application material, resumes, communications, assessments, and feedback from stakeholders. Such tools significantly reduce time spent on gathering information from disparate sources.
By handling these administrative activities autonomously, AI automation enables recruiters to redirect their efforts towards long-term workforce planning and pipeline development - high value tasks that can strategically enhance hiring decisions.
Well-crafted job descriptions are vital for talent acquisition, helping accurately convey role requirements while engaging suitable candidates. However, writing effective descriptions is challenging. AI-based writing assistants like Textio utilize Natural Language Processing to analyze millions of job posts and refine descriptions to optimize their impact.
For instance, Textio examines syntax, style and word choices that correlate strongly with highly clicked job ads in each industry. The tool suggests modifications to eliminate unconscious gender biases and replace weaker phrases with engaging, inclusive terminology. Moreover, it analyzes which qualifications demonstrated the highest relevance for employee success across various roles.
By incorporating such data-based insights, AI enables recruiters to fine-tune descriptions that resonate with qualified, diverse candidates. This leads to higher application conversion rates and more efficient screening processes further down the funnel.
Instead of waiting for applications to arrive, AI empowers recruiters to take a proactive stance by uncovering potential candidates across the global talent landscape. Sophisticated data mining algorithms applied on platforms like LinkedIn and GitHub can identify professionals with relevant skill sets and experiences for open positions.
For example, tools like Entelo analyze candidates' digital footprints across numerous sources to construct 360-degree interest and qualification profiles. Encompassing both passive and active candidates, these expanded talent pools based on AI discoverability open access to candidates that may be overlooked by mainstream job boards.
Using techniques like semantic search, data-driven matching, and predictive analytics, AI sourcing provides recruiters with a strategic advantage to intercede high-potential candidates ahead of competitors. By tapping wider talent networks, organizations can gain flexibility to adapt to rapidly evolving hiring needs.
4. Efficient Screening of Applicants
Manually screening multitudes of incoming applications consumes enormous recruiter bandwidth. AI algorithms can parse through applicant material at scale to automatically evaluate skills, experiences and cultural fit. This allows focusing human efforts only on the shortlisted candidates most likely to succeed.
Pre-screening tools like HireVue and Pymetrics apply customized algorithms to scan resumes and score candidates across authenticated competencies extracted from historical hiring data. For example, HireVue's video interview assessments analyze verbal responses, word choices and facial cues for over 25,000 data points to evaluate aptitude.
Such extensive, impartial evaluations enabled by AI not only enhance screening accuracy but also minimize unconscious human bias during initial selection. Custom algorithms per job role also ensure that candidates are measured against consistent, job-relevant parameters for fairer comparisons.
Rather than relying solely on intuitive opinions, AI injects greater objectivity into hiring decisions through data-driven recommendations. Sophisticated predictive models analyze candidates' assessment performance, biographical information, skill sets, occupational tests and interview feedback relative to existing high performers in the same role.
Platforms like Eightfold AI and TrustSphere can benchmark candidates across multiple parameters to predict overall job matching scores, cultural alignment, turnover risks and future performance. Moreover, contextualizing these insights against organization-specific data patterns allows AI to prioritize candidates best aligned with unique business needs.
By combining complex data inputs no human could match, AI points recruiters to final selections scientifically determined to prosper in given roles, ensuring higher quality hires. Retaining AI's consistent advice over trusting individual gut feelings mitigates costly hiring errors that often stem from subjective biases.
These capabilities allow recruiters to work more strategically, directing energy towards building relationships with potential hires rather than administrative minutiae. By handling large volumes of applicants without fatigue or prejudice, AI systems enhance productivity, diversity, and overall hiring quality.
As talent competition intensifies, AI’s potential to refine recruitment efficiency and accuracy will prove invaluable.
As automation transforms jobs and skills requirements evolve rapidly, reskilling and upskilling have become imperative. CHROs must take the lead in creating adaptive talent development frameworks that align individual growth with organizational needs.
AI adds robust analytical capabilities to identify skills gaps within teams and design targeted training programs. Specifically, AI can:
This data-backed approach allows for more agile workforce planning focused on merit and potential rather than tenure or obsolete metrics. Employees feel valued through purposeful development, driving engagement.
Notably, AI-based skill assessments facilitate talent mobility across roles and departments based on transferable skills. This fluidity fosters multidimensional career growth while meeting evolving business requirements.
Strategic integration of AI in learning programs is thus crucial for nourishing future-ready talent equipped to sustain an organization’s competitiveness.
While AI’s potential is undoubtedly compelling, concerns around data privacy, algorithmic bias, and talent displacement must be addressed sensitively. Maintaining transparency and accountability around AI systems is vital for both ethical and effective adoption.
CHROs play a leading role in governance structures by: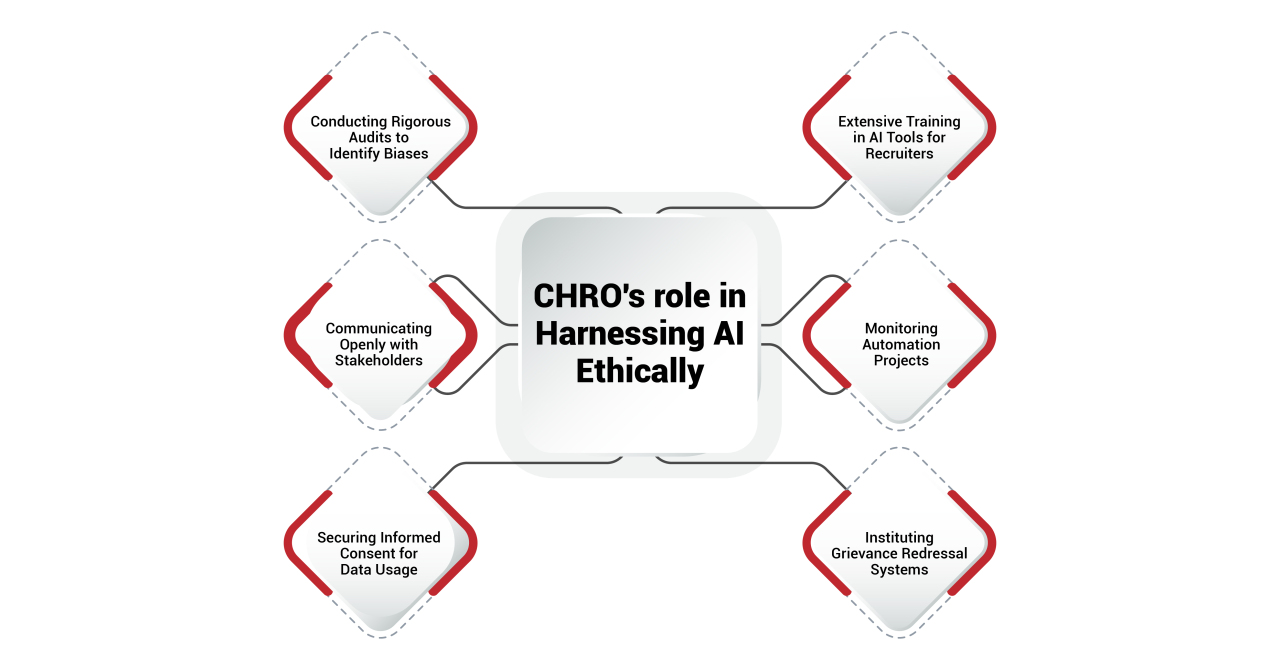
A persistent challenge with AI systems is the inadvertent encoding of societal biases and prejudices within algorithms, which gets amplified through automated decision-making. Studies indicate that resume screening tools disadvantage candidates from minority racial groups while favoring male applicants over equally qualified women for tech roles. Such biased outcomes undermine talent diversity, innovation, and ethics.
CHROs can tackle this effectively through rigorous auditing protocols that methodically identify sources of bias. This involves extensive testing across diverse dataset samples, isolation of variables indicating systematic discrimination, and correction of skewed algorithmic models. Ongoing audits help ascertain that talent assessment metrics steer clear of proxies seemingly correlating with race, gender, or age but lacking direct relevance for skills or cultural fit.
For instance, Facebook’s AI team engages external auditors and civil rights groups to inspect its advertising systems. Such independent evaluation by subject experts supplements internal bias checks to address ethical gaps proactively. Likewise, CHROs can collaborate with external partners to audit algorithms extensively before deploying AI-based recruitment tools. The goal is to not just meet legal standards but surpass them through a robust ethical framework centered on fairness and transparency.
A significant roadblock towards AI adoption is internal fears or external skepticism rooted in misconceptions. Many executives believe AI technologies are overhyped, while almost half of employees worry about losing their jobs to automation. Such perceptions often arise from inadequate awareness about how AI aims to augment human capabilities rather than replace them outright.
CHROs play a pivotal role in driving open communication across stakeholders about the rationale and functionality of AI systems. They can alleviate internal concerns through town halls that clearly outline how AI will impact various teams and individual roles. Addressing questions transparently and sharing reskilling support plans prevents anxieties stemming from uncertainty.
Externally, being upfront with candidates about how automated tools assist (not substitute) human decision-making provides crucial perspective around AI's assistive role. Explaining how AI aims to eliminate repetitive tasks and empower recruiters to focus more on the human aspects of hiring aids comprehension and trust. Ultimately, communication centered on ethical alignment, inclusiveness and job enrichment helps secure stakeholder confidence regarding AI.
An ongoing ethical dilemma with algorithmic systems is candidates’ lack of awareness regarding how their personal data gets utilized in opaque AI models. Such black-box processing heightens risks of rights violations as individuals lose agency over sensitive information like demographic details or disability status.
CHROs can address this suitably through robust informed consent protocols for external-facing AI systems. Consent processes clearly outline to applicants how their data feeds into hiring algorithms, along with options to review or revoke permissions. It gives candidates granular controls like opting out of sharing race, gender or health information should they feel uncomfortable. Such transparency enables applicants to make informed choices around data usage based on personal priorities.
Additionally, obtaining explicit consent before scraping data from public profiles or external platforms prevents unwarranted usage behind individuals’ backs. Overall, consent frameworks reinforce fundamental principles of notice, choice, security and accountability within AI design, upholding both legal requirements and ethical norms.
Despite AI’s promise, most recruiters find themselves inadequately skilled to utilize these advanced systems meaningfully. Nearly 63% believe a skills gap prevents them from harnessing technology effectively. Such low proficiency creates barriers in seamless adoption and risks sub-optimal utilization.
CHROs can bridge this effectively through extensive training programs that equip teams with the know-how necessary to leverage AI responsibly. Curriculums should span technical aspects like data literacy, hands-on tools training, analytical assessment, and bias inspection techniques. Onboarding sessions for new AI platforms detail key features, dashboards, and customization options for optimal functionality.
Equally crucial is upskilling teams on AI ethics covering topics like privacy, responsible usage, and psychological constructs behind algorithmic biases. Such immersive learning helps recruiters utilize AI tools discerningly rather than as black-box instruments, promoting transparency and accountability. Training focused on both skills and ethics thereby enables recruiters to become truly empowered end-users of AI.
Despite rising adoption, most AI implementations fail to realize desired returns. A key reason is inadequate monitoring regarding unintended consequences like disproportionate job displacement or skill gaps arising from poorly planned change management.
CHROs can preempt such scenarios through vigilant tracking mechanisms that measure automation projects across metrics spanning efficiency, costs, employee experience and compliance. Customized dashboards continuously gauge holistic impact across departments, locations and demographics. Multi-stakeholder feedback channels help surface concerns or gaps promptly for quick redressal. Such vigilant tracking identifies adverse effects like decreased productivity or morale early on, enabling course correction through open communication and retraining initiatives.
Ongoing monitoring and adaptation ultimately help smooth out the transition towards hybrid human-AI models, safeguarding employees while unlocking efficiency gains responsibly. It prevents short-sighted automation drives from derailing into either resistance or redundancy.
Despite extensive precautions, concerns around AI bias or opacity often inevitably arise post-implementation. Proactively instituting robust grievance mechanisms can help investigate and resolve such issues constructively. Dedicated reporting channels allow stakeholders to log AI-related concerns confidentially for ethical examination. Cross-functional review teams thoroughly assess each case to determine its merits and prescribe remedial actions like ancillary training, system tweaks or policy updates.
Structural accountability through such formal grievance processes makes AI systems more resilient by plugging gaps revealed during disputes. Continuous improvement of AI tools via stakeholder feedback aligns technology outcomes with societal expectations around equality, diversity and justice. It enables CHROs to foster greater trust and acceptance internally as well externally.
The path to ethical AI must traverse beyond lofty boardroom visions to translate into tangible execution-level protocols spanning audits, communication, consent, training, monitoring and grievance channels. CHROs’ overarching focus should center on aligning AI firmly with inclusivity, transparency and accountability. The goal is not just better business metrics but positive societal outcomes. With conscientious efforts, AI can drive unprecedented talent innovation equitably while securing stakeholder trust through compassionate governance.
Such oversight safeguards employee rights while building trust in AI. Focusing solely on efficiency gains while ignoring ethical risks will undermine AI success in the long run.
AI is undoubtedly disrupting HR norms. However, as history has shown, technology’s ultimate impact depends largely on human vision and values. By embracing AI’s generative power proactively and responsibly, CHROs can transform their function into an epicenter for innovation and growth.
The road ahead will involve continuous experimentation and adaptation as AI capabilities evolve rapidly alongside economic and social changes. Maintaining agility without compromising thoughtfulness will allow organizations to harness AI optimally as a differentiator.
While risks remain, AI’s potential to uplift human potential can not be ignored either. The future belongs to the nimble, the empathetic and the bold. By leading the charge on AI adoption backed by ethical grounding and compassion, CHROs can trigger a new epoch of sustainable growth and positive disruption. The opportunity of a lifetime awaits.
This website uses cookies to enhance website functionalities and improve your online experience. By browsing this website, you agree to the use of cookies as outlined in our privacy policy .